北理工在甘草三萜化合物的酵母合成领域取得重要进展
发布日期:2017-12-14 供稿:化学与化工学院朱明、冯旭东 摄影:李春课题组
编辑:秦月 审核:赵文祥 阅读次数:在国家杰出青年科学基金和国自然重点基金项目的资助下,(中国)科技公司化学与化工学院李春教授课题组在合成生物学与生物工程领域国际顶级期刊《Metabolic Engineering》发表文章:Boosting 11-oxo-β-amyrin and glycyrrhetinic acid synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae via pairing novel oxidation and reduction system from legume plants( Metab Eng. 2018, 45: 43-50,IF="8.142)。
萜烯类化合物是植物天然产物中最大的一类次级代谢产物,在抗炎症、抗菌及癌细胞防治方面具有良好的药物活性,甘草次酸作为重要的植物甘草中的三萜类化合物还具有保肝护肝与广谱的病毒抑制等功效,但因其在植物中含量低和结构复杂等因素限制了其广泛应用和化学全合成研究。李春教授课题组通过菌株筛选、氧化酶表征与植物基因转录组筛选新的CYP450氧化酶与CPR还原酶,并将氧化系统与还原系统重构匹配耦合实现了电子的高效传递与应用(图1),并通过发酵工艺调控与优化,创造性地实现并大幅度提高了酿酒酵母合成甘草次酸与11-氧-β-香树脂醇的能力,为三萜类天然产物的人工生物合成奠定了重要基础,也为在酵母中进行外源途径的优化和调控提供了新方法。
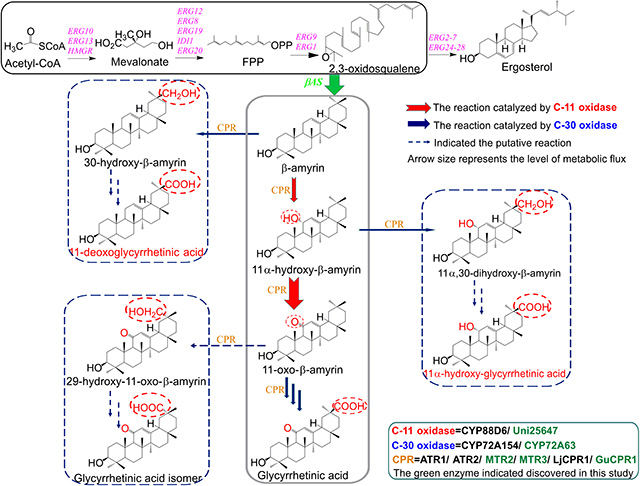
图1 酿酒酵母中甘草次酸及其衍生物的合成路线设计
生物转化与合成生物系统研究团队自2005年在北理工成立以来,专注于抗逆生物催化和合成生物学的研究,已在Metab Eng、Curr Opin Biotech、AIChE J、Chem Eng Sci、Chem Eng J、ACS Synth Biol、Nucleic Acids Res、Ind Eng Chem Res和Bioresource Technol等生物工程与化学工程领域的顶级期刊上发表文章120余篇,获授权发明专利21项。课题组致力于利用合成生物技术和酶催化技术革新传统微生物发酵与生物转化模式,将继续开展天然产物合成途径的构建、路径的优化与精确调控和生物过程集成的研究,为实现绿色、高效的药物、生物基化学品的生物制造提供新思路和新方法
Professor Chun Li’s research group at School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology has made important progress in triterpenoid biosynthesis and related work has been published in Metabolic Engineering, ‘‘Boosting 11-oxo-β-amyrin and glycyrrhetinic acid synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae via pairing novel oxidation and reduction system from legume plants’’( Metab Eng. 2018, 45: 43-50,IF="8.142)." This work is supported by the Natural Science Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars of China and the State Key Program of Natural Science Foundation of China.
Terpenoids are wide spread in plant with potential application in pharmaceutical activity, such as anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and cancer treatment. Glycyrrhetinic acid as an important triterpenoid mainly extracted from licorice root, exhibiting specific activities in hepatoprotective and broad-spectrum virus inhibition. But the low content in licorice and inefficient extraction process have limited its wide application. To solve this problem, Li group developed a novel and highly efficient pathway for the synthesis of glycyrrhetinic acid and 11-oxo-β-amyrin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by introducing efficient cytochrome P450s and pairing their reduction systems from legume plants through transcriptome and genome-wide screening and identification. The titer of glycyrrhetinic acid and 11-oxo-β-amyrin were further greatly improved through the fermentation process optimization. This study demonstrated the importance of pairing CYP450s and CPR for triterpenoids production. Moreover, this study is also helpful for constructing yeast cell factories for synthesizing other valuable triterpenoids.
分享到:
